Accuracy of Capillary Blood Glucose Test When Fasting in Diabetes Patients or General Population: Performance Evaluation of G300 Based on ISO 15197:2013 Standards
Article information
Abstract
Background
Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an important role in management of diabetes mellitus. Blood glucose measurement is based on using plasma glucose separated from whole blood, but many people with diabetes and health care providers use a portable glucose meter for convenience. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and agreement of G300 portable glucose monitoring system against standard venous glucose testing methods, based on ISO 15197:2013 standards.
Methods
This study was the evaluation of G300 system accuracy following ISO 15197:2013 standards. We estimated precision, system accuracy, hematocrit interference, interfering substances, and user performance.
Results
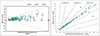
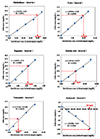
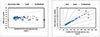
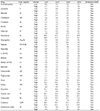
In repeatability precision evaluation of those glucometers, standard deviation was 2.9–3.7 mg/dL at glucose levels under 100 mg/dL and coefficient of variation was 1.7–3.2% at glucose levels over 100 mg/dL, respectively. In accuracy evaluation, 99.5% of difference values between results of G300 portable glucose monitoring system and clinical laboratory were within 95%. Consensus Error grid analysis showed that all values (100%) are within zone A. Hematocrit range between 20% and 60% did not cause interference. These results were acceptable for the ISO15197:2013 criteria in all glucose concentrations.
Conclusions
This study showed that G300 can provide reliable blood glucose results for patients and health care providers to manage diabetes mellitus, satisfying the ISO 15197:2013 criteria.
Notes
Research grant benefits : Green Cross Medical Science(IRB number : SCHUH 2016-10-016-004).