Evidence of Interventions for Preventing Obesity of Children and Adolescents Using Existing Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- Seolhye Kim1, Eunju Sung2, Sunmi Yoo3,
- Received August 28, 2016 Accepted December 22, 2016
- ABSTRACT
-
- Background
- Pediatric obesity is an important global issue in public health. However, previous efforts for childhood obesity prevention have sporadically been implemented in Korea, neither evidence-based nor with proper evaluation. We aimed to investigate the characteristics of an effective intervention for prevention of pediatric obesity by reviewing previous systematic reviews and Meta-analyses.
- Methods
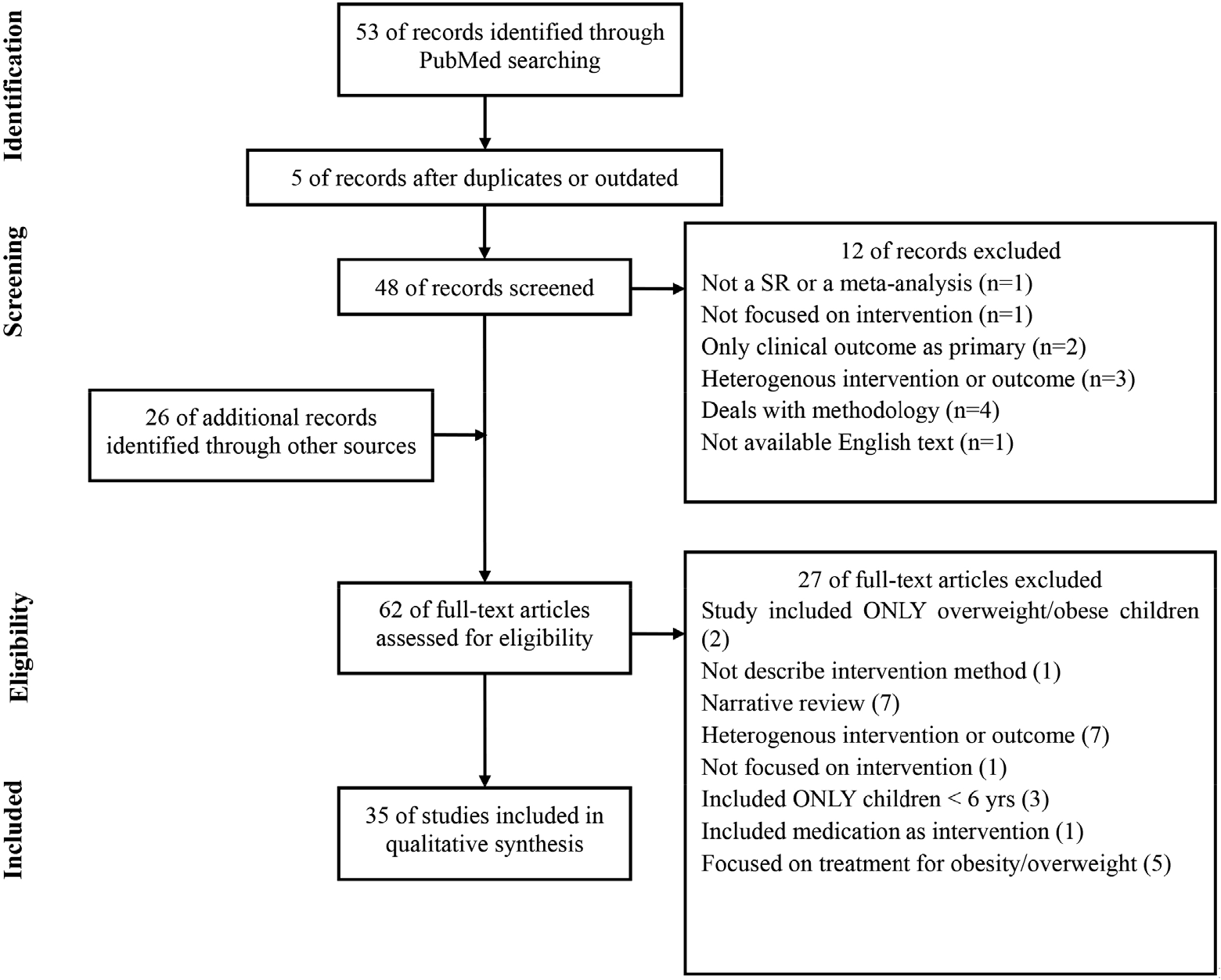
- PubMed was searched for articles published frombetween January 2005 to November 2015. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) articles published in English; (2) child and/or adolescents (between 2 and 18 years of age) as subjects; and (3) systematic reviews or meta-analyses concerning the preventive intervention of pediatric/adolescent obesity. Each study was evaluated via the Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews for quality assessment. We conducted a quantitative analysis to evaluate the implications, strengths, and limitations of each study.
- Results
- Our final analysis included 35 articles, of which 15 were systematic reviews and 20 were meta-analyses. Among these, 24 studies (69%) advocated the efficacy of preventive intervention for pediatric obesity. Multidimensional approach including diet, exercise, and environmental factors conducted in schools with a parent and community involvement wasis more effective at preventing obesity. The efficacy of intervention varied depending on the age, sex, region, and socioeconomic characteristics of participantssubjects.
- Conclusions
- Preventive intervention of pediatric obesity demonstrated smallminor improvements in body mass index and had positive effects on behavioral and clinical variables, which are associated with obesity. For the efficient prevention of pediatric obesity, it is necessary to consider efforts for developing various intervention programs, with active as well as the participation of school, family, and social community groups.
Table 1.
Abbreviations: AMSTAR, assessment of multiple systematic reviews; PRISMA, preferred reporting items for systematic reviews an meta-analysis; PA, physical activity; N, nutrition; C, combined nutrition and physical activity; y, year; mo, month; S, school; H, home; Cm community; Pc, primary care; Cc, child care; CHI, consumer health informatics; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; BF, bod fat; SFT, skin fold thickness; P, prevalence of obese or overweight; Ed, educational intervention; wk, week; Mod, moderate; SR, systematic re view; SB, sedentary behavior; Bwt, body weight; En, environment; NA, not assessed; FV, fruit and vegetables; MVA, moderate to vigorous a tivity; B, behavior; Ht, height; WHR, waist/hip ratio.
Table 2.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval; CHI, consumer health informatics; RR, relative risk; RCT, randomized controlled trial; HPS, health-promoting school; SDS, standard deviation score; MD, mean difference; ES, effect size; PICOS, population, interventions, comparators, main outcome, study design; PRISMA, preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis; PA, physical activity; CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Table 3.
Abbreviations: PA, physical activity; BMI, body mass index; CI, consumer health informatics; GRADE, the grading of recommendations assessments, developments and evaluation; OR, odds ratio; WMD, weighted mean difference; PICOS, population, interventions, comparators, main outcome, study design; ES, effect size.
- REFERENCES
- REFERENCES
References
1. World Health Organization. Population-based prevention strategies for childhood obesity: report of a WHO forum and technical meeting, Geneva, 15–17 December 2009 [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. [Accessed Dec 21, 2016]. Available from:. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44312/1/9789241599344_eng.pdf.2. Kim HR, Kang YH, Kwak NS, Kang EJ, Kim EJN. Trends in obesity and comprehensive policy strategy to prevent obesity in Korea [Internet]. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs; 2009. [Accessed Dec 21, 2016]. Available from:. http://repository.kihasa.re.kr. 8080/bitstream/201002/803/1/%ec% 97%b0%ea%b5%ac_2009–07.pdf..3. Lee HY. Effectiveness of Obesity management programs: systematic review and metaanalysis. Korean J Health Educ Promot 2007;24(4):131-46.4. Sung KS, Yoon YM, Kim EJ. Meta-analysis of the effects of obesity management program for children. Child Health Nurs Res 2013;19(4):262-9.
[Article]5. Shea BJ, Hamel C, Wells GA, Bouter LM, Kristjansson E, Grimshaw J, et al. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol 2009;62(10):1013-20.
[Article] [PubMed]6. Kim SY, Park JE, Seo HJ, Seo HS, Shon HJ, Shin CM, et al. NECA's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews and metaanalyses for intervention. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs; 2011.7. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, G⊘tzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and metaanalyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009;339:b2700.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]8. Budd GM, Volpe SL. School-based obesity prevention: research, challenges, and recommendations. J Sch Health 2006;76(10):485-95.
[Article] [PubMed]9. Cook-Cottone C, Casey CM, Feeley TH, Baran J. A meta-analytic review of obesity prevention in the schools: 1997–2008. Psychol Sch 2009;46(8):695-719.
[Article]10. Katz DL, O'Connell M, Njike VY, Yeh MC, Nawaz H. Strategies for the prevention and control of obesity in the school setting: systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32(12):1780-9.
[Article] [PubMed]11. Lavelle HV, Mackay DF, Pell JP. Systematic review and metaanalysis of school-based interventions to reduce body mass index. J Public Health (Oxf) 2012;34(3):360-9.
[Article] [PubMed]12. Luckner H, Moss JR, Gericke CA. Effectiveness of interventions to promote healthy weight in general populations of children and adults: a metaanalysis. Eur J Public Health 2012;22(4):491-7.
[Article] [PubMed]13. Marsh S, Foley LS, Wilks DC, Maddison R. Family-based interventions for reducing sedentary time in youth: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev 2014;15(2):117-33.
[Article] [PubMed]14. Stice E, Shaw H, Marti CN. A meta-analytic review of obesity prevention programs for children and adolescents: the skinny on interventions that work. Psychol Bull 2006;132(5):667-91.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]15. van Grieken A, Ezendam NP, Paulis WD, van der Wouden JC, Raat H. Primary prevention of overweight in children and adolescents: a metaanalysis of the effectiveness of interventions aiming to decrease sedentary behaviour. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2012;9:61.
[PubMed] [PMC]16. Wahi G, Parkin PC, Beyene J, Uleryk EM, Birken CS. Effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing screen time in children: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2011;165(11):979-86.
[Article] [PubMed]17. Chen JL, Wilkosz ME. Efficacy of technology-based interventions for obesity prevention in adolescents: a systematic review. Adolesc Health Med Ther 2014;5:159-70.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]18. Williams AJ, Henley WE, Williams CA, Hurst AJ, Logan S, Wyatt KM. Systematic review and metaanalysis of the association between childhood overweight and obesity and primary school diet and physical activity policies. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2013;10:101.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]19. Osei-Assibey G, Dick S, Macdiarmid J, Semple S, Reilly JJ, Ellaway A, et al. The influence of the food environment on overweight and obesity in young children: a systematic review. BMJ Open 2012;2(6):): e001538..
[Article]20. Brown T, Summerbell C. Systematic review of school-based interventions that focus on changing dietary intake and physical activity levels to prevent childhood obesity: an update to the obesity guidance produced by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Obes Rev 2009;10(1):110-41.
[Article] [PubMed]21. Branscum P, Sharma M. After-school based obesity prevention interventions: a comprehensive review of the literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2012;9(4):1438-57.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]22. Connelly JB, Duaso MJ, Butler G. A systematic review of controlled trials of interventions to prevent childhood obesity and overweight: a realistic synthesis of the evidence. Public Health 2007;121(7):510-7.
[Article] [PubMed]23. Doak CM, Visscher TL, Renders CM, Seidell JC. The prevention of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: a review of interventions and programmes. Obes Rev 2006;7(1):111-36.
[Article] [PubMed]24. Gonzalez-Suarez C, Worley A, Grimmer-Somers K, Dones V. School-based interventions on childhood obesity: a metaanalysis. Am J Prev Med 2009;37(5):418-27.
[PubMed]25. Harris KC, Kuramoto LK, Schulzer M, Retallack JE. Effect of school-based physical activity interventions on body mass index in children: a metaanalysis. CMAJ 2009;180(7):719-26.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]26. Kamath CC, Vickers KS, Ehrlich A, McGovern L, Johnson J, Singhal V, et al. Clinical review: behavioral interventions to prevent childhood obesity: a systematic review and metaanalyses of randomized trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93(12):4606-15.
[PubMed]27. Kropski JA, Keckley PH, Jensen GL. School-based obesity prevention programs: an evidencebased review. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16(5):1009-18.
[Article] [PubMed]28. Lissau I. Prevention of overweight in the school arena. Acta Paediatr 2007;96(454):12-8.
[Article] [PubMed]29. Niemeier BS, Hektner JM, Enger KB. Parent participation in weight-related health interventions for children and adolescents: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Prev Med 2012;55(1):3-13.
[Article] [PubMed]30. Peirson L, Fitzpatrick-Lewis D, Morrison K, Ciliska D, Kenny M, Usman Ali M, et al. Prevention of overweight and obesity in children and youth: a systematic review and metaanalysis. CMAJ Open 2015;3(1):E23-33.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]31. Sbruzzi G, Eibel B, Barbiero SM, Petkowicz RO, Ribeiro RA, Cesa CC, et al. Educational interventions in childhood obesity: a systematic review with metaanalysis of randomized clinical trials. Prev Med 2013;56(5):254-64.
[Article] [PubMed]32. Silveira JA, Taddei JA, Guerra PH, Nobre MR. The effect of participation in school-based nutrition education interventions on body mass index: a metaanalysis of randomized controlled community trials. Prev Med 2013;56(3–4):237-43.
[Article] [PubMed]33. Sobol-Goldberg S, Rabinowitz J, Gross R. School-based obesity prevention programs: a metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013;21(12):2422-8.
[Article] [PubMed]34. Vasques C, Magalhães P, Cortinhas A, Mota P, Leitão J, Lopes VP. Effects of intervention programs on child and adolescent BMI: a metaanalysis study. J Phys Act Health 2014;11(2):426-44.
[Article] [PubMed]35. Wang Y, Cai L, Wu Y, Wilson RF, Weston C, Fawole O, et al. What childhood obesity prevention programmes work? A systematic review and metaanalysis. Obes Rev 2015;16(7):547-65.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]36. Waters E, de Silva-Sanigorski A, Hall BJ, Brown T, Campbell KJ, Gao Y, et al. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;12:CD001871..
[Article] [PubMed]37. Zenzen W, Kridli S. Integrative review of school-based childhood obesity prevention programs. J Pediatr Health Care 2009;23(4):242-58.
[Article] [PubMed]38. Langford R, Bonell CP, Jones HE, Pouliou T, Murphy SM, Waters E, et al. The WHO health promoting school framework for improving the health and wellbeing of students and their academic achievement. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;4:CD008958..
[Article] [PubMed]39. Bleich SN, Segal J, Wu Y, Wilson R, Wang Y. Systematic review of community-based childhood obesity prevention studies. Pediatrics 2013;132(1):e201-10.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]40. Showell NN, Fawole O, Segal J, Wilson RF, Cheskin LJ, Bleich SN, et al. A systematic review of home-based childhood obesity prevention studies. Pediatrics 2013;132(1):e193-200.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]41. Li M, Li S, Baur LA, Huxley RR. A systematic review of school-based intervention studies for the prevention or reduction of excess weight among Chinese children and adolescents. Obes Rev 2008;9(6):548-59.
[Article] [PubMed]42. Friedrich RR, Schuch I, Wagner MB. Effect of interventions on the body mass index of school-age students. Rev Saude Publica 2012;46(3):551-60.
[PubMed]43. Brown HE, Atkin AJ, Panter J, Corder K, Wong G, Chinapaw MJ, et al. Family-based interventions to increase physical activity in children: a metaanalysis and realist synthesis protocol. BMJ Open 2014;4(8):): e005439..
[Article]44. Swinburn B, Gill T, Kumanyika S. Obesity prevention: a proposed framework for translating evidence into action. Obes Rev 2005;6(1):23-33.
[Article] [PubMed]