Continuous Abstinence Rates from Smoking Over 12 Months according to the Frequency of Participation in a Hospital-based Smoking Cessation Program among Patients Discharged after Acute Myocardial Infarction
Article information
Abstract
Background
This study evaluated the continuous abstinence rates from smoking at 12-month after a hospital-based smoking cessation program was applied for smokers hospitalized for acute myocardial infarction.
Methods
Among those who are hospitalized for acute myocardial infarction from January 2012 to December 2013, ninety-eight smokers agreed to quit smoking were eligible for follow up to 12 months. Each of them underwent six consecutive sessions (first during admission, the other 5 sessions after discharge) of behavioral modification, counseling for withdrawal symptoms, and anti-smoking advices by a trained nurse. Exhaled carbon monoxide measurements less than 6 ppm were used to confirm the smoking cessation status of each participant.
Results
Mean age of all participants was 55.2±10.8 years old, and their continuous abstinence rates at 1, 3, 6, 12 months were 63.3%, 49.0%, 43.9%, and 37.8% for each. The continuous abstinence rate from smoking after 12 months was 69.7% and significantly higher in those who completed the 6 sessions than 21.5% in those who completed 5 sessions or less (P<0.001). After adjustment for general and smoking-related characteristics, multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that full participation relative to 5 or less participation was significantly associated with higher continuous abstinence rate from smoking at 12 months (odds ratio: 7.96; 95% confidence interval: 2.07–30.55).
Conclusions
The consistency of participating in a hospital-based smoking cessation program, described herein, significantly improved success rates of smoking cessation in patients discharged after acute myocardial infarction. Hospital-based smoking cessation program based on education and counseling should be included as an important part of patient management for acute myocardial infarction.
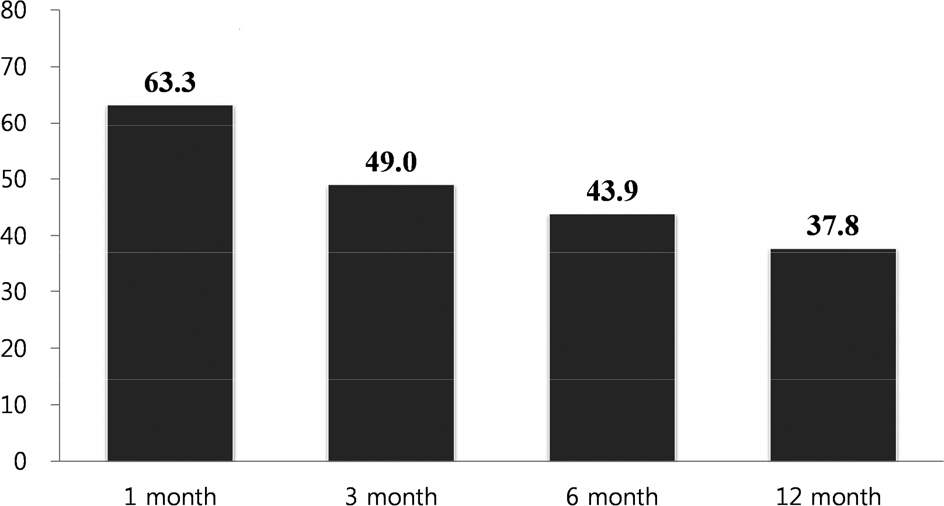
Continuous abstinence rates from smoking decreased from 63.3% at 1 month to 37.8% at 12 month in patients discharged after acute myocardial infarction who participated in hospital-based smoking-cessation program.
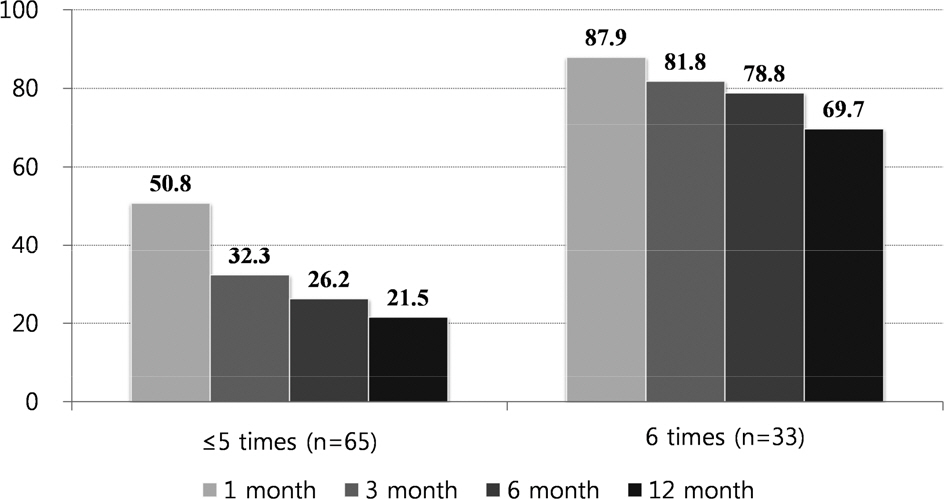
Continuous abstinence rates from smoking were higher in patients discharged after acute myocardial infarction who participated in smoking-cessation program of 6 times versus ≤5 times.

General characteristics of subjects according to the frequency of participating in smoking cessation program

Smoking-related characteristics of subjects according to the frequency of participating in smoking cessation program
