Analytic Performance Evaluation of Blood Monitoring System G400 according to ISO 15197:2013
Article information
Abstract
Background
Self-monitoring of blood glucose is an important component of therapy for diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to evaluate the analytic performance evaluation of blood monitoring system G400 according to ISO 15197:2013.
Methods
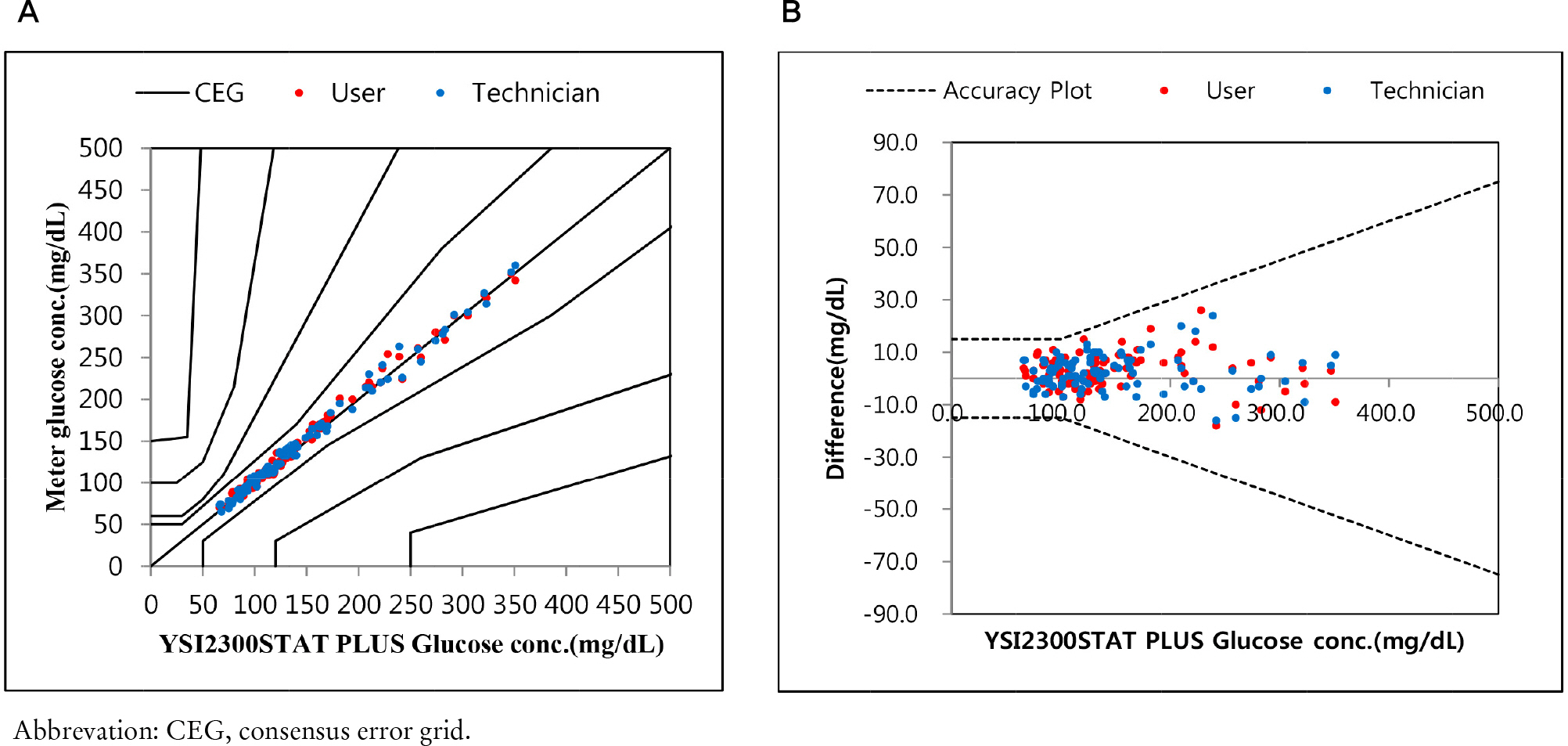
We evaluated the G400 according to the ISO 15197:2013 guideline, we measured precision, accuracy, interference of hematocrit and interfering substances, user performance.
Results
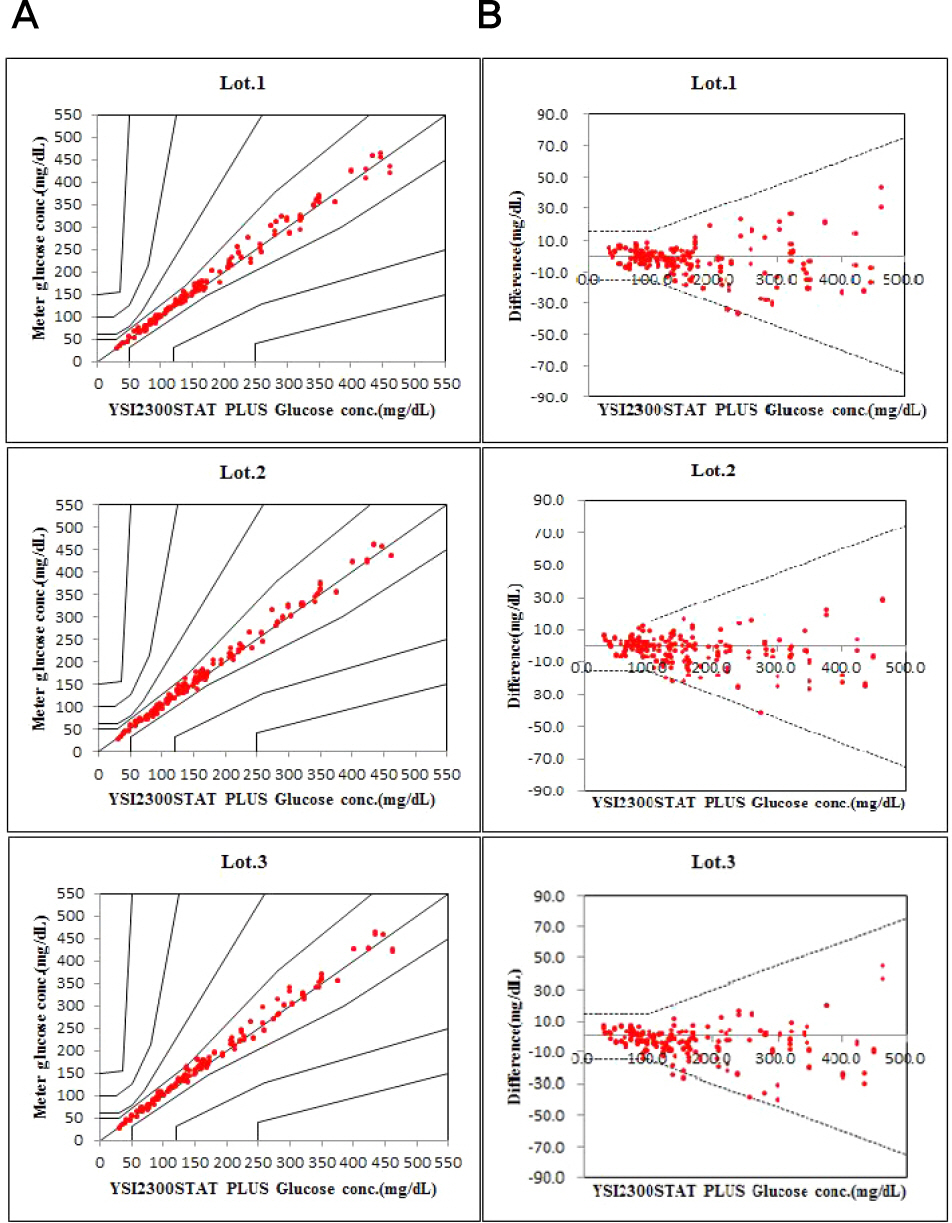
Repeatability and intermediate precision of G400 showed standard deviation 2.7–3.8 mg/dL, 2.4–3.6 mg/dL and coefficient of variation 1.9–2.9% and 1.7–3.7%, respectively. Accuracy measured 98–98.5%, satisfied acceptable criteria. Error grid analysis showed that all results of this study were in zone A. Hematocrit between 20% to 60% did not cause interference. Three of 24 interfering substances were not acceptable criteria, and dose-response evaluation was needed.
Conclusions
This study showed that G400 was considered reliable results satisfying the ISO 15197:2013 criteria
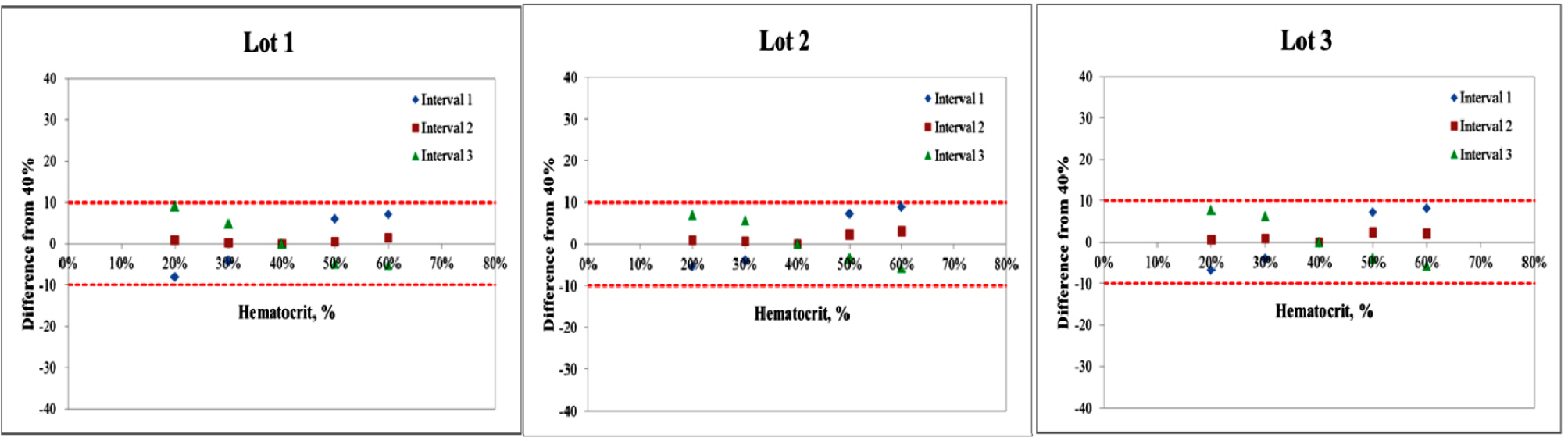
Interference of hematocrit. The two bold lines represent the acceptance criteria: ±10 mg/dL of the results at glucose concentrations <100 mg/dL, ±10% of the results at glucose concentrations ≥100 mg/dL. Interval 1 is 30–50 mg/dL, interval 2 is 96–144 mg/dL, interval 3 is 280–420 mg/dL.