References
1. World Health Organization. WHO global report on falls prevention in older age Geneva: WHO Press; 2008.
2. Morse J. Enhancing the safety of hospitalization by reducing patient falls. Am Infect Control 2002;30(6):376–80.
3. Perrell KL, Nelson A, Goldman RL, Luther SL, Prieto-Lewis N, Rubenstein LZ. Fall risk assessment measures: an analytic review. J Gerontol A Biol Sci 2001;56(12):M761–6.
4. DiBardino D, Cohen ER, Didwania A. Meta-analysis: multidisciplinary fall prevention strategies in the acute care inpatient population. J Hosp Med 2012;7(6):497–503.
5. Hitcho EB, Krauss MJ, Birge S, Claiborne Dunagan W, Fischer I, Johnson S, et al. Characteristics and circumstances of falls in a hospital setting. J Gen Intern Med 2004;19(7):732–9.
6. Ledford L. Research-based protocol: prevention of falls Iowa City: University of Iowa Gerontological Nursing Intervention Research Center; 1997.
7. Stalenhoef PA, Diederiks JP, Knottnerus JA, Kester AD, Crebolder HF. A risk model for the prediction of recurrent falls in community-dwelling elderly: a prospective cohort study. J Clinl Epidemiol 2002;55(11):1088–94.
8. The Victorian Quality Council. Minimizing the risk of falls & fall-related injuries: Guidelines for acute, subacute and residental care setting [Internet] Melbourn Victoria: The Metropolitan Health and Aged Care Services Division Victorian Government Department of Human Services; 2004. [Accessed March 10, 2015].
http://www.health.vic.gov.au/qualitycoun-cil/downloads/falls/research.pdf.
9. Morse JM. Computerized evaluation of a scale to identify the fall-prone patient. Can J Public Health 1986;77(Suppl 1):21–5.
10. Schmid NA. Reducing patient falls: A research-based comprehensive fall prevention program. Mil Med 1990;155(5):202–7.
11. Hendrich A, Nyhuuis A, Kippenbrock T, Soga ME. Hospital falls: Development of a predictive model for clinical practice. Appl Nurs Res 1995;8(3):129–39.
12. Oliver D, Britton M, Seed P, Martin FC, Hopper AH. Development and evaluation of an evidence based risk assessment tool (STRATIFY) to predict which elderly inpatients will fall: case-control and cohort studies. BMJ 1997;315(7115):1049–53.
13. Poe SS, Cvach M, Dawson BP, Straus H, Hill EE. The Johns Hopkins fall risk assessment tool: Postimplementation evaluation. J Nurs Care Qual 2007;22(4):293–8.
14. Korea Hospital Nurses Association. Safety management guidelines for nursing 6th ed.th ed. Seoul: Hospital Nurses Association; 2005.
16. Matarese M, Ivziku D, Barttolozzi F, Piredda M, De Marinis MG. Systematic review of fall risk screening tools for older patients in acute hospitals. J Adv Nurs 2015;71(6):1198–209.
17. Aranda-Gallardo M. Morales-Asencio JM, Canca-Sanchez JC, Barrero-Sojo S, Perez-Jimenez C, Morales-Fernandez A, et al. Instruments for assessing the risk of falls in acute hospitalized patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis. BMC Health Serv Res 2013;13:122.
18. Billington J, Fahey T, Galvin R. Diagnostic accuracy of the STRATIFY clinical prediction rule for falls: a systematic review and metaanalysis. BMC Fam Pract 2012;7(13):76.
19. Harrington L, Luquire R, Vish N, Winter M, Wilder C, Houser B, et al. Meta-analysis of fall-risk tools in hospitalized adults. J Nurs Adm 2010;40(11):483–8.
20. Muir SW, Berg K, Chesworth B, Klar N, Speechley M. Quantifying the magnitude of risk for balance impairment on falls in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Clin Epidemiol 2010;63(4):389–406.
21. Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy version 1.0 [Internet] London: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2010. [Accessed May 30, 2013].
http://srdta.cochrane.org/.
22. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and metaanalyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 2009;151(4):264–9.
23. Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 2011;155(8):529–36.
24. Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan KS, Coomarasamy A. Meta-DiSc: a software for metaanalysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol 2006;6:31.
25. Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med 2000;45(1–2):23–41.
26. Walter SD. Properties of the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test data. Stat Med 2002;21(9):1237–56.
27. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a metaanalysis. Stat Med 2002;21(11):1539–58.
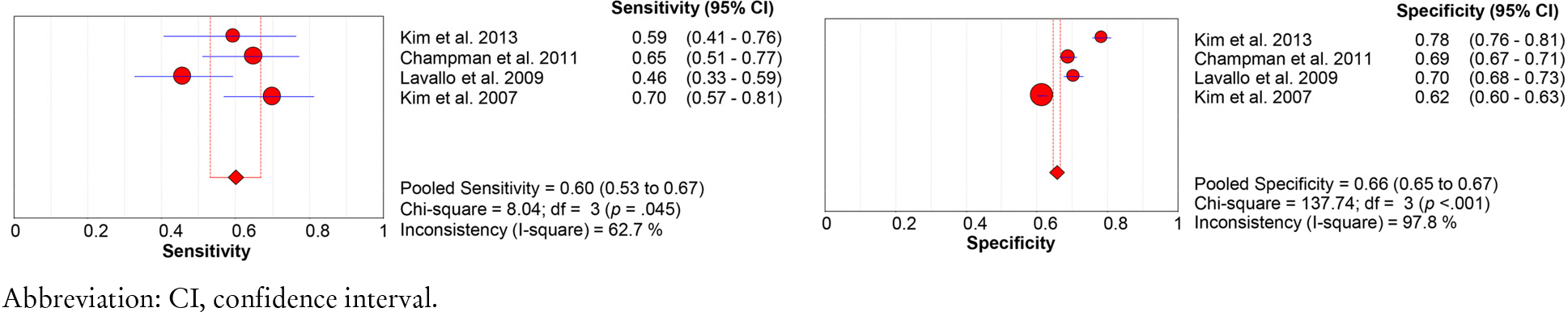
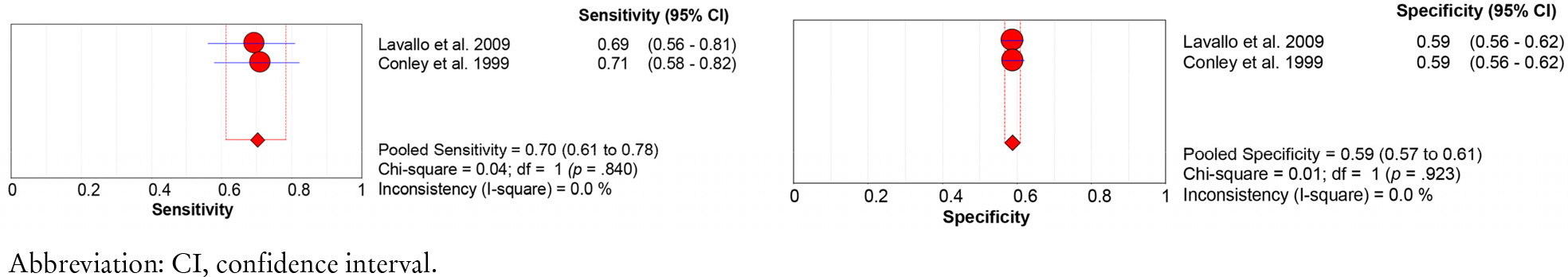
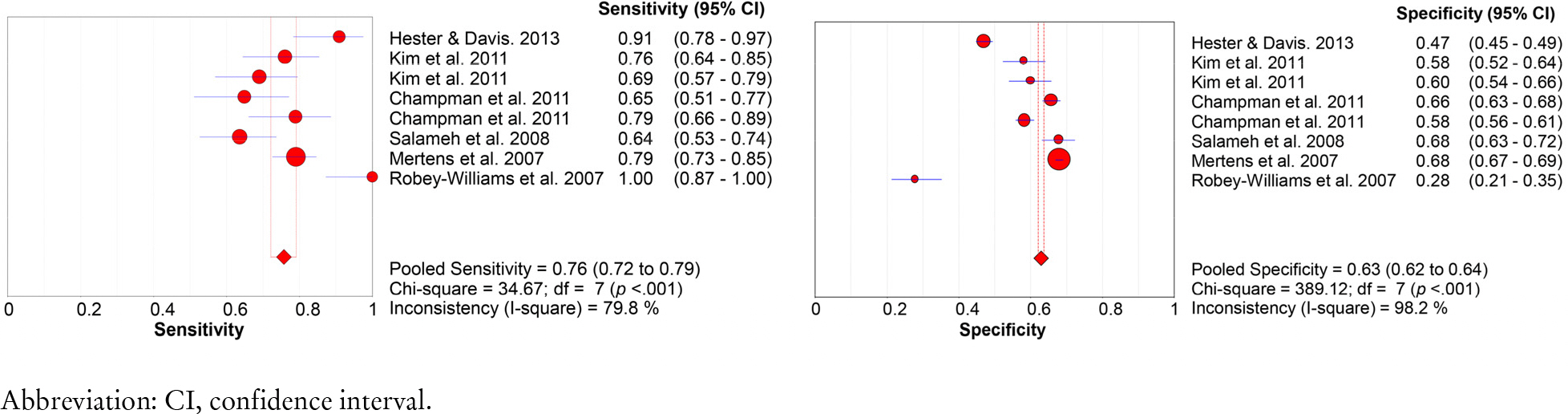
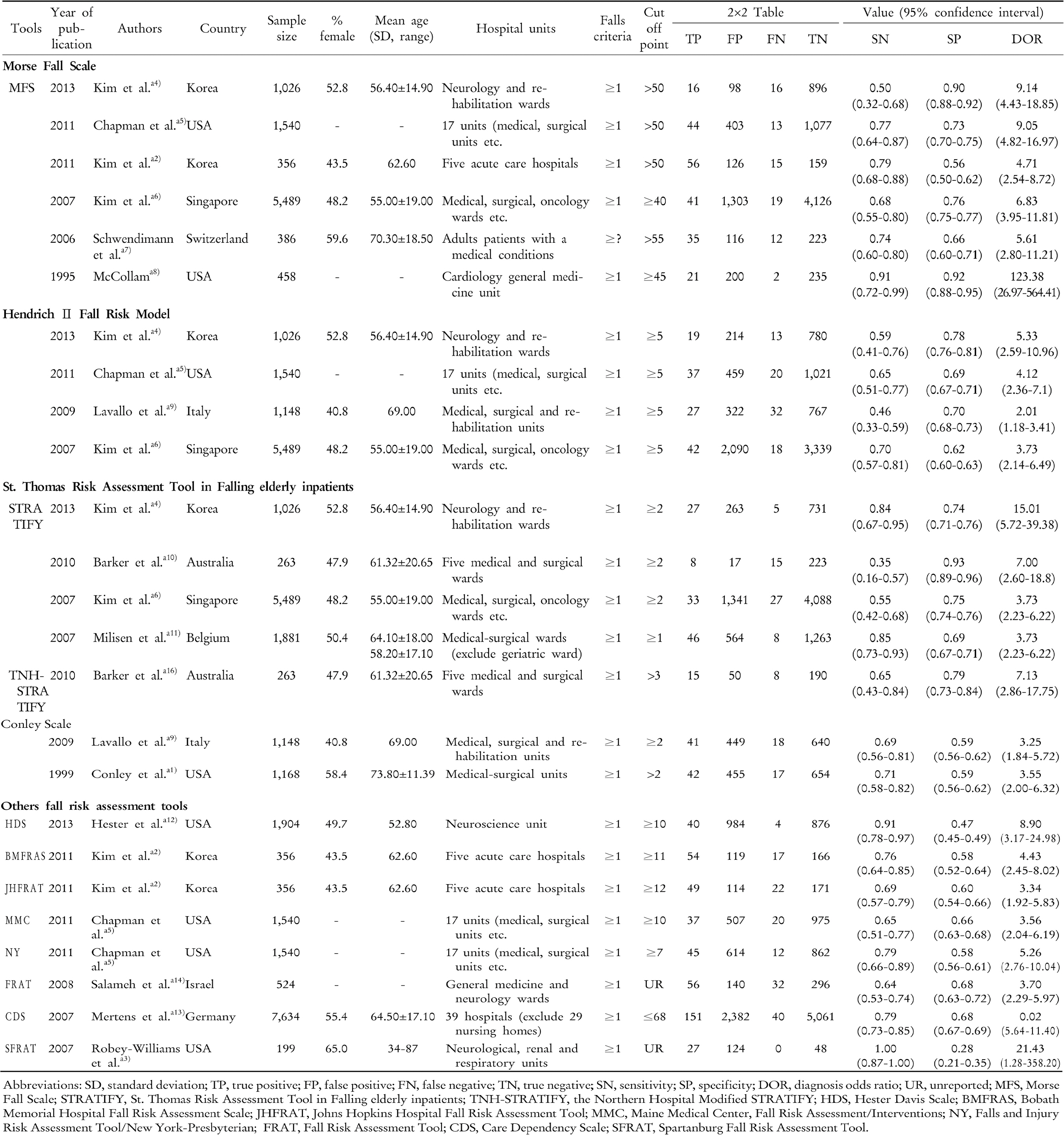
28. Park SH, Choi YK, Hwang JH. Predictive validity of the STRATIFY for fall screening assessment in acute hospital setting: a metaanalysis. Korean J Adult Nurs 2015;27(5):559–71.
29. Morse JM, Morse RM, Tylko SJ. Development of a scale to identify the fall-prone patient. Can J Aging 1989;8(4):366–77.
30. Morse JM. Predicting fall risk. Can J Nurs Res 1998;30(2):11–2.
31. Kim KI, Jung HK, Kim JC, Kim SK, Cho HH, Kim DY, et al. Evidence-based Guideline for Fall Prevention in Korea. Korean J Med 2015;89(6):752–80.