| Korean J Health Promot > Volume 19(4); 2019 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background
Methods
Results
REFERENCES
Table┬Ā2
Association between lung function and serum uric acids based on a simple linear regression model

Table┬Ā3
Association between lung function and serum uric acids based on a multiple linear regression model
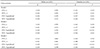
Model 1 was adjusted for age and BMI. Model 2 was adjusted for age, BMI, and smoking. Model 3 was adjusted like model 2 plus SBP, DBP, and FBS levels.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBS, fasting blood sugar; FEV1 %predicted, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in the first second; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC %predicted, percent predicted forced vital capacity; FVC, forced vital capacity; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Table┬Ā4
Association between lung function and serum uric acids by male smoking status based on a multiple linear regression model

Model 1 was a simple linear regression analysis. Model 2 was adjusted for age and BMI. Model 3 was adjusted like model 2 plus SBP, DBP, and FBS levels.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBS, fasting blood sugar; FEV1 %predicted, percent predicted forced expiratory volume in the first second; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC %predicted, percent predicted forced vital capacity; FVC, forced vital capacity; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 773 View
- 3 Download
- Related articles
-
Relationship between Changes in Body Mass Index and Pulmonary Function in Adults2011 September;11(3)
The Relationship Between AHI and Serum Ferritin in Male Snorers2009 September;9(3)




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print


